Generalized structure computer network
Computer networks are the highest form of multi-machine associations. Let us highlight the main differences between a computer network and a multi-machine computing complex.
The first difference is the dimension. A multi-machine computing complex usually includes two, maximum three computers, located mainly in one room. A computer network can consist of tens and even hundreds of computers located at a distance from each other from several meters to tens, hundreds and even thousands of kilometers,
The second difference is the division of functions between computers. If in a multi-machine computing complex the functions of data processing, data transmission and system control can be implemented in one computer, then in computer networks these functions
distributed among various computers.
The third difference is the need to solve the problem of message routing in the network. A message from one computer to another in the network can be transmitted along different routes depending on the state of the communication channels connecting the computers to each other.
Combining into one set of funds computer technology, communication equipment and
Data transmission channels impose specific requirements on the part of each element of a multi-machine association, and also require the formation of special terminology.
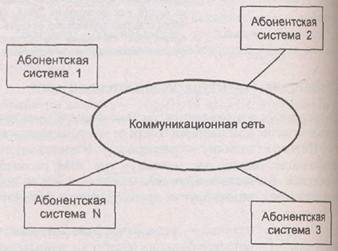
Network subscribers- objects that generate or consume information on the network.
Subscribers networks can be individual computers, computer complexes, terminals, industrial robots, numerically controlled machines, etc. Any network subscriber connects to the station. Station- equipment that performs functions related to the transmission and reception of information.
The set of subscriber and station is usually called subscriber system. To organize the interaction of subscribers, a physical transmission medium is required.
Physical transmission medium- communication lines or space in which they propagate electrical signals, and data transmission equipment.
Based on the physical transmission medium, it is built communication network
which ensures the transfer of information between subscriber systems.
This approach allows us to consider any computer network as a collection
subscriber systems and communication network. Generalized structure of a computer network
is shown in Fig. 6.3.
Rice. 63. Generalized structure
computer network
Applied informatics set information technologies used to process information related to practical activities. Technology activities related to the application of scientific research results for the creation and use of material and spiritual values. Informatization of society the process of creating optimal conditions to meet the information needs of citizens and organizations based on the use of information technologies. Computer universal device for information processing.
Share your work on social networksIf this work does not suit you, at the bottom of the page there is a list of similar works. You can also use the search button
Other similar works that may interest you.vshm>
|
| 10929.
|
|
Subject and basic concepts of computer science |
13.39 KB |
|
|
Computer science is complex technical science which systematizes methods for creating storage, reproduction, processing and transmission of data by means of computer technology, as well as the principles of operation of these means and methods of managing them. The emergence of computer science is due to the emergence and spread new technology collection, processing and transmission of information related to recording data on computer media. The main task today includes the following main areas of computer science for practical application... |
| 4464.
|
|
Basic concepts and methods of computer science and coding theory |
31.67 KB |
|
|
Signals, data, information; information as a subject of computer science study; properties of information; classification of information. The concept of economic information, its properties. Structure of economic information. Classification of economic information. |
| 7974.
|
|
BASIC INFORMATION ABOUT MEASUREMENTS. BASIC CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS |
39.54 KB |
|
|
Definition of concepts metrology standardization certification Metrology is the science of measurements on ways to achieve the required accuracy and reliability of the correct recording of results to ensure the uniformity of measurements. Technical measurements using working measuring instruments. Metrological measurements using standards and exemplary measuring instruments. They cannot be used in areas subject to the requirement of uniformity of measurements. |
| 10419.
|
|
Computer science concept. Subject and tasks of computer science |
17.64 KB |
|
|
There is a lot of information in the world: written, spoken, visual. Until recently, information carriers were language, various material surfaces, paper, etc. Now we are gradually moving to digital storage of information. Why is this necessary? Firstly, information storage becomes less voluminous. |
| 6303.
|
|
Basic requirements for the selection and synthesis of catalysts. Composition of contact masses. Main types of promoters. Concepts about the active component, carrier (matrix) and binder of heterogeneous catalysts and adsorbents |
23.48 KB |
|
|
Along with the chemical composition, an active catalyst requires a high specific surface area and an optimal porous structure. Note that to obtain a highly selective catalyst, a high specific surface area is not necessary. In particular, it is desirable to minimize the deposition of coke on the surface of the catalyst in organic reactions and to maximize the period of operation of the catalyst before regeneration. The preparation of the catalyst should be highly reproducible. |
| 8399.
|
|
Inheritance. Basic Concepts |
41.01 KB |
|
|
Each object is a specific representative of a class. Objects of the same class have different names but the same data types and internal names. Objects of the same class have access to the same class functions and the same operations configured to work with class objects to process their data. And new classes are formed on the basis of base classes by derived classes, descendants, and child classes. |
| 6723.
|
|
Basic concepts of labor physiology |
34.25 KB |
|
|
Labor and work. Labor is the expedient activity of people to create use values. As a social category, labor is determined by social, economic and production relations in society. |
| 14763.
|
|
Basic Project Management Concepts |
17.7 KB |
|
|
Basic concepts of project management A project is a set of activities or work distributed over time aimed at achieving a set goal. Achieving this result signifies the successful completion and completion of the project. For example, for a building construction project, the result is the building itself accepted for operation. Like the beginning, the end of a project can be specified prescriptively or calculated when drawing up a work plan. |
| 2194.
|
|
Basic concepts of creativity psychology |
225.11 KB |
|
|
Creativity from English Initially, creativity was considered as a function of intelligence and the level of intelligence development was identified with the level of creativity. Subsequently, it turned out that the level of intelligence correlates with creativity up to a certain limit, and too high an intelligence hinders creativity. Currently, creativity is considered as a function of a holistic personality that is not reducible to intelligence and depends on a whole complex of its psychological characteristics. |
| 2131.
|
|
Basic concepts of component technologies |
231.84 KB |
|
|
This is a rather arbitrary and abstract element of the system structure, isolated in a certain way from the environment, solving some subtasks within the framework of the general tasks of the system and interacting with the environment through a certain interface. Component diagrams in the UML language often depict components that are units of assembly and configuration management; files with code in some language; binary files; any documents included in the system. Sometimes components representing deployment units also appear there... |
Modern humanity practically cannot imagine its life without computers, but they appeared not so long ago. Over the past twenty years, computers have become an integral part of all areas of activity, from office needs to educational needs, thereby creating the need to develop capabilities and develop accompanying software. Connecting computers into a network has made it possible not only to increase but also to reduce the cost of their maintenance, as well as to reduce time. In other words, computer networks have two goals: sharing software and equipment, as well as provision open access to data resources. Computer networks are built on the client-server principle. In this case, the client is an architectural component that, using a login and password, uses the capabilities of the server. The server, in turn, provides its resources to other network participants. This could be storage, creating a shared database, using input/output facilities, etc. There are several types of computer networks: Local; Regional; Global. Here it would be fair to note on what principles the various Organization of local computer networks Typically, such networks bring together people who are at close range, so they are most often used in offices and enterprises for storing and processing data, transmitting its results to other participants. There is such a thing as “network topology”. Simply put, this is a geometric diagram of connecting computers into a network. There are dozens of such schemes, but we will consider only the basic ones: tire, ring and star. 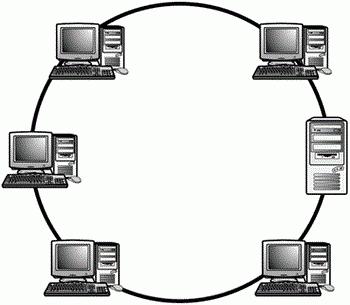
- A bus is a communication channel that connects nodes into a network. Each node can receive information at any convenient time, and transmit only if the bus is free.
- Ring. With this topology, the working nodes are connected sequentially in a circle, that is, the first station is connected to the second and so on, and the last is connected to the first, thereby closing the ring. The main disadvantage of this architecture is that if at least one element fails, the entire network is paralyzed.
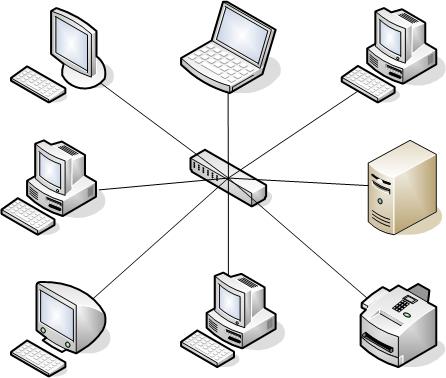
- A star is a connection in which the nodes are connected by rays to the center. This connection model comes from those distant times when computers were quite large and only the head machine received and
As for global networks, everything is much more complicated. Today there are more than 200 of them. The most famous of them is the Internet. Their main difference from local ones is the absence of a main management center. Such computer networks operate according to two principles: Server programs located on network nodes that serve users; Client programs located on user PCs and using server services. Global networks give users access to various services. You can connect to such networks in two ways: through a dial-up telephone line and via a dedicated channel.
Computer network is a method of electronic interaction between two or more computers through a data transmission medium for the purpose of receiving and transmitting information.Her purpose– ensuring shared access to common resources: hardware, software and information.
 Basic Concepts A computer that has access to shared resources is called client
.Working group– these are several computers working on one project within a local
networks, which include a dedicated server.Server(host computer)
– a fairly powerful computer on which all shared resources and special software for managing access to the entire network are located.
 Computer network separation based on territorial location:LAN - local area networks;MAN - Metropolitan Area Networks;WAN - global networks (Wide Area Networks);
 1) Local networks The local network(LS) - several computers connected to each other and concentrated in a small space (room, premises, building, group of buildings).Coaxial cables are used as the transmission medium. High transfer speed - from 1 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s.
 2) City networks City networks cover a group of buildings and are implemented on fiber optic or broadband cables. According to their characteristics, they are intermediate between local and global networks.
 3) Global networks Global networks - a network of computers remote over considerable distances (for example, the Internet).Analogue or digital wire channels, as well as satellite communication channels (usually for communication between continents), are used as the transmission medium.Limitations on transmission speed (up to 28.8 Kbit/s on analogue channels and up to 64 Kbit/s on user sections of digital channels).
 Classification of computer networks Separation according to the interaction model network devices:Peer-to-peer(single-layer) networksHierarchical(networks with dedicated server)
 by area of operation(banking networks, networks of scientific institutions, university networks);by form of functioning(commercial networks and free networks, corporate and public networks);by the nature of the functions being implemented(computational, informational, mixed);
 Other classification features of computer networks by control method(networks with decentralized, centralized and mixed control);software compatibility Networks can be homogeneous or homogeneous (consisting of software-compatible computers) and heterogeneous or heterogeneous (computers included in the network are software incompatible).
 Network topology Topology determines the geometric placement (configuration) of network nodes and the method of connections between them in the data transmission medium.3 basic types network topology:"tire", "star", "ring".
 Bus topology IN tire In a (linear) topology, all computers are connected to one common cable, called a bus or backbone.(+) prevalence and popularity, low cost, high flexibility and data transfer speed, ease of network expansion;(–) vulnerability to physical damage to the cable, because the location of the fault is difficult to locate.
 Ring topology ring, when all network nodes are connected to one closed ring channel .
Information along the ring can be transmitted only in one direction and all connected computers can participate in its reception and transmission.(+) ease of implementationdevices,(–) low reliability
 Star topology star-shaped, when all network nodes are connected to one central node, called a host or hub.(+) high level of data protection in the central node, simplifying the search for fault localization.(–) significant cable consumption
 Characteristics of the communication channel Bandwidth communication channel is the speed of information transfer over the network, determined by the type of network adapters and cables used. Measured in butts(bit/second).long-distance channels (satellite, fiber optic) have a capacity of 2 million baud or higher.a leased line (an ordinary copper pair of telephone wire running without switches from machine to machine) can transmit, depending on the length (no more than a few kilometers), from 64 to 256 Kbaud.dial-up (regular telephone lines) have different bandwidths, and mobile phone lines allow the modem to operate at a speed of no higher than 9600 baud.
 Layers of Computer Interconnection (OSI)
 1 - Physical layer Physical layer(Physical Layer) - level of control of the transmitting medium. The medium can be “twisted pair”, optical fiber, coaxial cable, radio channel, analog telephone channel, etc., each such medium defines its own rules for communicating with it.
 2 - Channel level Data Link Layer(Data Link Layer) controls the transfer of data over the communication channel.Main functions:splitting the transmitted data into portions called frames,separating data from a stream of bits transmitted at the physical layer for processing at the network layer,transmission error detection;recovery of incorrectly transferred data.
 3 - Network layer Network layer(Network Layer) manages the network, communication on the network between machines, the problem of addressing and routing data is solved here.
 4 - Transport layer Transport layer(Transport Layer) provides reliable transmission (transportation) of data between computer systems on the network for higher layers. Here the problems of data transfer management and related tasks are solved: error localization and processing, and data transfer itself.
 5 - Session level Session layer(Session Layer) ensures the interaction of programs. This solves problems of synchronizing data transfer, confirming/setting passwords, etc.
 6 – Executive level Data presentation layer(Presentation Layer) solves the problem of data presentation.Main functions:data code conversion,their encryption/decryption,compression of transmitted data.
 7 - Application layer Application layer(Application Level) solves the problems of standardizing interaction with application systems.Main functions:network management;synchronization of interacting application tasks;performing system application tasks (e-mail, file sharing).
 Data transfer protocol Protocol is a set of definitions (agreements, rules) regulating the format and procedures for the exchange of information between two or more independent devices or processes.
 Internet protocol family usually divided into:Low-level (describing the technical details of the presentation and transmission of information), For example: 2 TCP/IP protocolsHigh-level (describing the meaningful interpretation of this information in different operating systems).
 Higher level protocols FTP - File Transfer ProtocolThe client sends requests to the server that resemble commands for working with the OS file structure (directories and files). The server executes these commands (moving from directory to directory, viewing the contents of directories, copying files from a directory on the server machine to the current directory on the client machine and back).HTTP - HTML file transfer protocolThe protocol is implemented by the WWW (World Wide Web) service. HTML (HyperText Markup Language) stands for hypertext markup language.
 Internet Internet is a union of transnational computer networks operating using various protocols, connecting all kinds of computers, physically transmitting data across all available types lines – from twisted pair and telephone wires to fiber optic and satellite channels. We can say that the Internet
is a network of networks that entangles the entire globe.
 Network addressing IP address, which consists of four numbers from 0 to 255.For example, 128.250.33.190The rightmost number indicates the number of the specific computer. The remaining numbers, depending on the address class, correspond to the numbers of networks and local subnets. The first number of a computer’s IP address determines whether it belongs to a particular class of network:class A addresses - a number from 0 to 127;Class B addresses - a number from 128 to 191;Class C addresses - a number from 192 to 223.
 Network addressing DNS(domain name system) - domain name system.For example, win.smtp.dol.ruThe very first name on the left in the name is the name of the real computer that has the IP address, followed by the name of the group that assigned the name to this computer, then the name of a larger group, etc. The domain name system has a hierarchical structure.Top level domains there are two types:geographical(two-letter)administrative(three-, four-letter)
 Uniform Resource Locator (URL) URL(Universal Resource Locator) - the web page address includes the document access protocol, the domain name or IP address of the server on which the document is located, as well as the path to the file and the file name itself: protocol://domain name/path/ filename.For example, http://schools.keldysh.ru/info2000/index.htm
 Internet services Service is a pair of programs that interact with each other according to certain rules called protocols. One of the programs in this pair is called a server, and the other is called a client. The corresponding technology is called " client-server».
 1.
Electronic mail (e-mail) Provides for the transmission of messages from one user with a specific computer address to another.E-mail address consists of two parts separated by the @ symbol: username@servername.The postal service is based on two protocols:SMTP– correspondence is sent from the computer to the server,POP3– receiving incoming messages.Email programs– Microsoft Outlook Express, Netscape Messenger, The Bat! Mail service on Yandex, Rambler, Mail.
 2. World Wide Web (WWW) The WWW service is a single information space consisting of hundreds of millions of interconnected electronic documents stored on web servers. Individual documents are called web pages. Groups of thematically linked web pages are called websites. Purposeful movement between web documents is called web navigation.Programs for viewing web pages are called browsers. The main function of a web browser is to display hypertext. Hypertext allows you to structure a document by highlighting link words (hyperlinks) in it.Browser examples– Internet Explorer, Opera, Netscape Navigator, Safari, FireFox.
 3. File archives The FTP service is responsible for receiving and transferring large files. It has its own servers on the global network on which data archives are stored. These archives may be commercial or restricted, or may be publicly available.Files become available for work (reading, execution) only after copying to your own computer.File archive servers: freeware.ru, www.freesoft.ru, www.download.ru
 4. Teleconferences (Usenet) Usenet is a worldwide discussion board. It consists of a collection of conferences whose names are organized hierarchically according to the topics discussed.Messages are sent to these conferences by users using special software. After sending, messages are sent to news servers and become available for reading by other users.To read and send messages, use news readers: Netscape News or Internet News.
 5. IRC Service IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a relayed Internet chat designed for direct communication between several people in real time. This service is also called chat.The most common client programs are mIRC, Pirch, MS Chat and Virc for Windows and Homer or Ircle for Macintosh.
 6. Search the World Wide Web Internet search servers are divided into two groups:general purpose search engines(databases containing thematically grouped information about the information resources of the World Wide Web. Such search engines allow you to find websites or web pages by keywords in the database or by searching in a hierarchical directory system);specialized search engines.
 The structure of search engines Stage 1- collecting information from the WWW using special programs called spiders, crawlers or spiders;Stage 2- indexing of words in the form of a special database;Stage 3- processing the client's request and providing him with search results in the form of a list of hyperlinks.
 Russian search engines www.rambler.ruwww.yandex.ruwww.aport.ruwww.google.ru
 Foreign search engines
 Geographic domains of the 1st level

LOCAL COMPUTER NETWORKS. TOPOLOGY. FEATURES OF BUILDING AND MANAGEMENT
Local computing network unites subscribers located at a short distance from each other (within 10-15 km). Typically, such networks are built within the same enterprise or organization.
Information systems built on the basis of local computer networks provide solutions to the following tasks:
- data storage;
- data processing;
- organizing user access to data;
- transfer of data and the results of their processing to users.
Computer networks implement distributed data processing. Here, data processing is distributed between two entities: the client and the server. During data processing, the client generates a request to the server to perform complex procedures. The server executes the request and sends the results to the client. The server provides storage of public data, organizes access to this data, and transmits the data to the client. This model of a computer network is called client-server architecture.
Based on the distribution of functions, local computer networks are divided into peer-to-peer and two-rank (hierarchical networks or networks with a dedicated server).
In a peer-to-peer network, computers have equal rights in relation to each other. Each user on the network decides for himself which resources of his computer he will provide for public use. Thus, the computer acts both as a client and as a server. Peer-to-peer sharing of resources is quite acceptable for small offices with 5-10 users, combining them into a work group.
A two-rank network is organized on the basis of a server on which network users register.
For modern computer networks, a mixed network is typical, combining workstations and servers, with some of the workstations forming peer-to-peer networks, and the other part belonging to two-peer networks.
Geometric connection diagram (configuration physical connection) network nodes is called the network topology. There are a large number of network topology options, the basic ones being bus, ring, and star.
- Tire.The communication channel connecting nodes into a network forms a broken line - a bus.
Any node can receive information at any time, and transmit only when the bus is free. Data (signals) are transmitted by the computer to the bus. Each computer checks them, determining who the information is addressed to, and accepts the data if it is sent to it, or ignores it. If computers are located close to each other, then organizing a network with a bus topology is inexpensive and simple - you just need to lay a cable from one computer to another. Signal attenuation with increasing distance limits the length of the bus and, therefore, the number of computers connected to it. Bus topology problems arise when a break occurs (contact failure) anywhere in the country; network adapter
- one of the computers fails and begins to transmit signals with noise to the bus; you need to connect a new computer.Ring. The nodes are connected into a closed curve network. Data transmission is carried out in only one direction. Each node, among other things, implements the functions of a repeater. He receives and transmits messages, and perceives only those addressed to him. Using a ring topology, you can connect a large number of nodes to the network, solving the problems of interference and signal attenuation by means network card
each node.
- Disadvantages of a ring organization: a break at any point in the ring stops the operation of the entire network; the message processing time is determined by the time of sequential operation of each node located between the ruler and the message recipient; Due to the flow of data through each node, there is a possibility of unintentional distortion of information.Star.
The network nodes are connected to the center by rays. All information is transmitted through the center, making it relatively easy to troubleshoot and add new nodes without interrupting the network. However, the cost of organizing communication channels here is usually higher than for a bus and ring.
The combination of basic topologies - hybrid topology - provides a wide range of solutions that accumulate the advantages and disadvantages of the basic ones. In addition to the problems of creating local computer networks, there is also the problem of expanding (merging) computer networks. The fact is that created at a certain stage of development information system design features network components impose strict restrictions on the number of nodes and geometric dimensions of the network.
The following devices are used to connect local area networks.
1. Repeater- a device that provides amplification and filtering of a signal without changing its information content. As the signals travel along communication lines, they fade.
2.Repeaters are used to reduce the effect of attenuation. Moreover, the repeater not only copies or repeats received signals, but also restores the characteristics of the signal: it amplifies the signal and reduces interference. Bridge - a device that performs the functions of a repeater for those signals (messages) whose addresses satisfy pre-imposed restrictions. One of the problems large networks is tense
network traffic
(message flow on the network). This problem can be solved as follows.
A computer network is divided into segments. The transmission of messages from segment to segment is carried out only purposefully if a subscriber of one segment transmits a message to a subscriber of another segment. A bridge is a device that restricts movement across a network and prevents messages from passing from one network to another without confirming the right to cross.
Bridges can be local or remote.
Local bridges connect networks located in a limited area within an existing system.
Remote bridges connect geographically dispersed networks using communication channels and modems. Local bridges, in turn, are divided into internal and external.
3.Internal bridges are usually located on one computer and combine the function of a bridge with the function of a subscriber computer. Expansion of functions is carried out by installing an additional network card. External bridges involve the use of a separate computer with special software treatment. Router is a device that connects networks different types
4. , but using one- a special hardware and software complex designed to ensure compatibility between networks using different communication protocols.
The gateway converts the presentation form and data formats when transmitting them from one segment to another. The gateway performs its functions at a level above the network level. It does not depend on the transmission medium used, but depends on the data exchange protocols used. Typically a gateway performs conversions between protocols. With the help of gateways you can connect a local computer network
|