Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Tips How to infect Divx Updater
- Problems when using two operating systems and uninstalling one of them
- Boot in UEFI mode or legacy BIOS mode
- RAM Volumes and channels
- How to restore Windows if there are no restore points
- Charging a mobile phone with one battery
- How to increase volume through apps
- How to disable the Protect protection system in the Yandex Browser
- PGP encryption: what is it and how to use it
- avi file won't play - how to fix it
Advertising
| Name of 1 computer. The very first computer in the world - who created it? History of the ENIAC project |
|
The very first people to whom the word computer was used were people who performed all calculation operations in their heads, and they lived back in 1613. But later, with the advent of the 19th century, humanity began to realize that if machines for computing appeared, they could cope with work faster and would not require rest. It is believed that the very first computer in the world was created by a mathematician born in England, his name was Charles Babbage. His machine is recognized as the first device capable of automatically performing calculations and printing the results on paper. But due to financial problems, the scientist was never able to create the final version. The first computers of the twentieth century
Despite the fact that the first development was created a very long time ago, a full-fledged computer was assembled only in 1938. The very first electromechanical binary machine was introduced to the world, and it was invented by Konrad Zuse, a scientist from Germany. He called this computer Z1, but in the same year another device was built that emulated human actions, which followed a certain algorithm of instructions, and all the results obtained were displayed on a paper tape. This device was called a Turing machine, as it was invented by another scientist, Alan Turing. The very first computer officially recognized
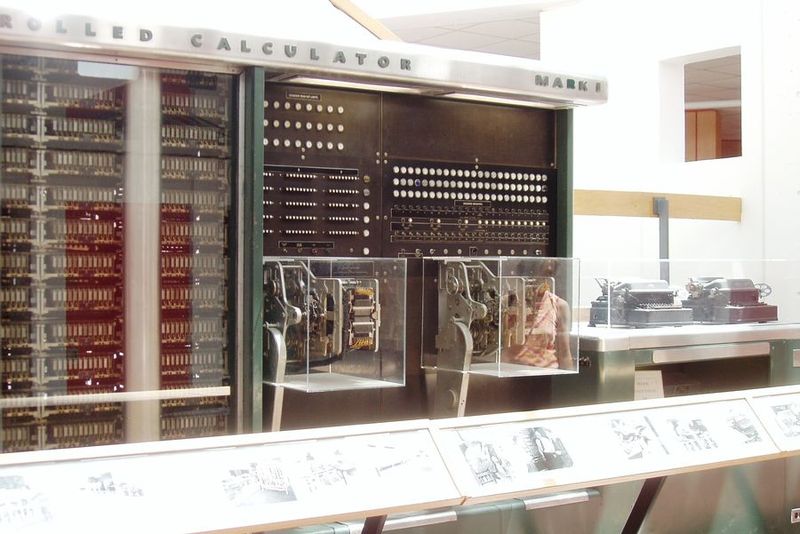
The officially registered very first computer is considered to be the Mark-1 programmable machine. Initially, her main goal was to serve for the benefit of the military. After a series of tests, which were successful, the computer was put into operation in 1944. It was created by IBM engineers and Harvard mathematician Howard Aickson. They took the work of Charles Babbage as a basis and began assembling it on the territory of that same Harvard. The world was presented with both the very first computer and the most expensive one - its price was 500 thousand dollars. The device consisted of more than 760,000 parts, its length was 17 m, and the body was made of glass and stainless steel. Considering the height of 2.5 meters, it was decided to allocate a separate room for it. As for the remaining characteristics of the very first computer (electronic computer), they are as follows:
Some inventors saw the first computer as a large and powerful adding machine. This opinion was held by those people who believed that the ENIAC device became the impetus for the development of all further computers. But the one who invented the Mark-1 is still considered its founder, thanks to the machine’s ability to automatically perform the required tasks.
The main advantage of the Mark-1 was the ability to perform the following tasks:
But soon the characteristics of the computer did not meet the inflated requirements of customers, so Howard Aiken proposed creating computers of a more powerful and modern type. After that, scientists released 3 more versions of one of the very first computers, the last model of which was created in 1952. ENIAC
All the first computers were invented for approximately the same purposes. Both in terms of characteristics and external data, they did not differ radically (you can compare “Mark-1” and “ENIAC” using numerous photos from the Internet). But if we talk about the computer created in 1945, it was already distinguished by its multitasking and increased level opportunities. But since the war was over this year, the car was not used for military purposes. It was decided to use the machine for other purposes, for example, to simulate the activation of a hydrogen bomb. Although the device was assembled later than its predecessor, the computer was just as huge, but its price was slightly less, and the machine included more than 17,000 lamps in its design. World-famous electronics engineers John Mosley and his partner John Eckert worked on the creation of this giant. To protect the structure from damage, it was decided to increase reliability by applying the same principle that was used at that time for musical electric organs. This helped to have a positive effect on reducing the accident rate, after which, out of a huge number of lamps, within 7 days, only 2-3 pieces could deteriorate. At that time, scientists invented best device for computing, its characteristics were as follows:
It took 200,000 man-hours to assemble the world's most advanced computing machine. Before the ENIAC machine, no computer had ever used a tabulator to enter and exit data from the computer. The only significant drawback of this device was its enormous size and weight - it exceeded the Mark-1 computer by several times in weight and 2 times in size. EDVAC
Soon Eckert and Mosley began their next invention, the EDVAC. Electronics engineers figured out how to make the first machine that would carry out calculations not only using punched cards, but also relying on programs located in its memory. These possibilities became available after the creation and further use of mercury tubes. And with the help binary system The issue of computers using a huge number of lamps and the use of complex calculation algorithms was resolved. Thus, the computer era advanced one more step; the device was assembled from the following elements:
The computers that were the predecessors no longer looked like the fastest when EDVAC appeared. To add sums, multiply and divide, a fraction of a second was enough for him, although he still occupied a fairly large area - about 46 square meters. meters. But the number of lamps, compared to ENIAC, decreased by 14,000 pieces, and the power was increased to 50 kW.
Quantum computer
Everyone already roughly understands when the first computer appeared, but what about a quantum device? A pleasant surprise was the recent development of Russians and scientists from America. For the first time in the world, they were able to assemble a quantum computer and successfully test it. On this moment a more complex quantum device has not yet been created. This kind of large-scale achievement allowed Russian scientists to become leaders in the race to create a full-fledged quantum machine. Such devices are special computing mechanisms that consist of qubits, in this case 51 pieces, and standard modules for calculations - they store a spectrum of values found in the interval between 0 and 1. Several more scientists from different countries. It was believed that the person closest to its creation was Google representative John Martinis. But still, Russian scientists, together with the Americans, were able to get ahead of everyone. They noticed that sets of atoms that are held inside laser cages and have a very low temperature could be used as quantum qubits. It was the use of this technology in a quantum device that could bring domestic scientists to a leadership position in the global market. It is not yet known what the situation with the cost of such a machine will be, but one cannot yet expect a low price, given the capabilities and complexity of the device. Conclusion
The first computers that went on mass sale were devices from Apple - they bore little resemblance to a modern computer. But it is thanks to all the developments of that time that now almost every resident of the country can afford a computer. Very soon, with the arrival quantum computers, humanity will be one step closer to stunning discoveries and the creation of the ideal computer. From Apple) creates a personal computer and receives a patent for it! Did you know that the world's first personal computer was created not by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in a Palo Alto garage, but by a simple Soviet designer Arseny Anatolyevich Gorokhov at the Omsk Research Institute of Aviation Technologies? Let's rewind time. 1950s. Computers are huge, bulky and expensive. The Soviet "Whirlwind" of 1951, the first machine with data output to the screen, has only 100% RAM. 512 bytes, occupies a two-story house. American "peer" - Univac– has a magnetic metal tape drive, a high-speed printer, but weighs 13 tons and costs about $1.5 million. Bendix G-15, released in 1956, is called a mini-computer - in fact it weighs 450 kg and costs at least $50,000. Not a single car deserves the title of personal car. 1960s. Computers are becoming faster, more powerful, and more compact. The first commercial computer equipped with a keyboard and monitor is released in the USA - "PDP-1". The dimensions of the new device are the size of three refrigerators, the price is tens of times lower than the cost of a conventional one. large computer. A big step forward, but not enough for the widespread introduction of technology. Total only 50 copies were sold. The first “home” computer claims to be Honeywell Kitchen Computer, introduced in the US in 1969. It weighed about 65 kg, cost 10600$ , was a pedestal with a built-in cutting board, a panel of lights and buttons. It performed only one function - storing various recipes. To work with the “kitchen computer,” two-week courses were required, because recipes were displayed on the screen in binary code. There were no people willing to purchase such an expensive “cookbook”. 1970s. With the creation of the first microprocessor, an era begins personal computers. Inventors compete to build their own models. American entrepreneur Edward Roberts is the first to realize how great the potential of the 8-bit microprocessor is. Intel 8080, released in 1974, and creates a microcomputer based on it "Altair 8800". Thanks to a deal concluded with Intel for the wholesale purchase of microprocessors ($75 per unit, with a retail price of $360), Roberts sets a record price for his invention - only 397 “buckets”! Advertising on the cover of a respected magazine "Popular Electronics" behind 1975 the year is doing its job. In the first month, developers sell several thousand copies "Altair 8800". However, the received order comes as a surprise to buyers: the kit consists of a set of parts and a box for the case. Users have to solder, test, and create programs in machine language themselves. (Which, of course, is also not bad, because it is on "Altair 8800" founders "Microsoft" Bill Gates and Paul Allen are testing their famous program - "Basic"). Be that as it may, Roberts’ computer is a godsend for inventors, and “mere mortals” are still left without technology. To help them in 1976 year, Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs come, deciding to sell their "Apple I" , assembled for personal use in a garage in Palo Alto (California). The cost of a new computer is 666,66$ . And the main advantage is that, unlike "Altair 8800" and many other cars of that time, "Apple I" offered already assembled. All you need is a case, a keyboard and a monitor. But they will also be included in the kit 2 years later, in the serial production of color, sound "Apple II". This is the history of the personal computer. Stop, stop, stop... But what about the Soviet scientist and the Research Institute of Aviation Technologies?! Oh yes! Completely forgot. There are in the history of personal computers and dark page. Here is how it was. In the distance 1968 year, 8 years before the first Apple, Soviet electrical engineer Arseny Anatolyevich Gorokhov invented the car entitled “Device for specifying a program for reproducing the contour of a part.” So, in any case, it is indicated in the patent, copyright certificate № 383005 , dated May 18, 1968. The name is not accidental, because the developed device was intended primarily for creating complex engineering drawings. The inventor himself prefers to call the device a “programmable device intellect.” According to the drawings, the “intellector” had a monitor, a separate system unit With hard drive, a device for solving autonomous problems and personal communication with a computer, motherboard, memory, video card and other things, with the exception of a computer mouse. Omsk electromechanical engineer Arseny Gorokhov 45 years ago invented a device that is now called a Personal Computer According to the website “Omsk Time”, today, unfortunately, it is impossible to see the world’s first personal computer, the institution where it was created is “ Mailbox» Omsk Research Institute of Aviation Technologies, closed for several years. The author of the invention still has patent, with description "Programmable intellect device" and an entry in the Russian book of records DIVO: 45 years ago in 1968, Omsk electromechanical engineer Arseny Gorokhov invented a device that is now called a Personal Computer. Now Gorokhov uses his personal computer mainly as a typewriter. According to him, it was new 5 years ago, and to do an “upgrade”, that is, to modernize, is expensive, the pension will not be enough. The components of a modern computer - a monitor, a system unit, a keyboard - were also in Gorokhov’s “intellector,” although under different names. The device was intended primarily for creating complex engineering drawings. Gorokhov also developed his own “software” - a way to dialogue with a machine without thick packs of punched cards and a team of programmers. But further All-Union patent things didn’t work out - the invention was not given the green light, and in 1975 they learned that the term “personal computer” was given to the world by the American company Apple. 40 copyright certificates and patents of Arseny Gorokhov over three decades are just moral satisfaction from his work. Traces of material remained in the patent records - 20 rubles for each, not included in the series. If a new product was still allowed to make its way into the “series,” the author received 1000 times more. Just to recognize the mysterious "law of luck" The inventor did not always succeed. And now Gorokhov calculates the probable profits from the opposite, not “how much they received, but how much they could not.” “It is not oil that is the future of Russia, but inventors”- the leitmotif of Gorokhov’s next article, “The System for Accelerated Development of Inventions,” published in the last, 12th, 2003 issue of the magazine “Intellectual Property.” It is a pity that in Russia there is no practice, like in the United States, where the President meets with the head of the Patent Office twice a year. Increasingly, instead of a sense of pride, one has to use irony, says the author. Prospects are fading. Now on the inventor’s desktop is a new type of periodic table, and a blank for spatial television. It’s just that there were no people interested in the idea, except for rare guest journalists. About the invention cell phone article “The Mystery of the Cell”... When did the first computers appear? It is not so easy to answer this question, since there is no single correct classification of electronic computers, as well as formulations of what can be classified as them and what cannot. First mentionThe word "computer" was first documented in 1613 and meant a person who performs calculations. But in the 19th century, people realized that a machine never gets tired of working, and it can do work much faster and more accurately. To begin counting the era of computing machines, the year 1822 is most often taken. The first computer was invented by the English mathematician Charles Babbage. He created the concept and began manufacturing the difference engine, which is considered the first automatic computing device. She was capable of counting multiple sets of numbers and making a printout of the results. But, unfortunately, due to funding problems, Babbage was never able to complete its full version. But the mathematician did not give up, and in 1837 he introduced the first mechanical computer, called the Analytical Engine. It was the very first general purpose computer. At the same time, his collaboration with Ada Lovelace began. She translated and supplemented his works, and also made the first programs for his invention. The Analytical Engine consisted of the following parts: an arithmetic-logical unit, an integrated memory unit and a device for monitoring the movement of data. Due to financial difficulties, it was also not completed during the scientist’s lifetime. But Babbage's designs and designs helped other scientists who created the first computers. Almost 100 years laterOddly enough, over the course of a century, computers have made almost no progress in their development. In 1936-1938, German scientist Konrad Zuse created the Z1, the first electromechanical programmable binary computer. Then, in 1936, Alan Turing built a Turing machine.
It became the basis for further theories about computers. The machine emulated the actions of a person following a list of logical instructions and printed the result of the work on a paper tape. The Zuse and Turing machines are the first computers in the modern sense, without which the computers we are accustomed to today would not have appeared. Everything for the frontThe Second World War also influenced the development of computers. In December 1943, the Tommy Flowers Company introduced a secret machine called the Kollos, which helped British agents break German message codes. It was the first all-electric programmable computer. The general public learned about its existence only in the 70s. Since then, computers have attracted the attention of not only scientists, but also the ministries of defense, which actively supported and financed their development.
There is some debate about which digital computer should be considered the first. In 1937-1942, University of Iowa professor John Vincent Atanasoff and Cliff Berry (graduate student) developed their ABC computer. And in 1943-1946 J. Presper Eckert and D. Mauchly, scientists at the University of Pennsylvania, built the most powerful ENIAC weighing 50 tons. Thus, Atanasov and Berry created their machine earlier, but since it was never fully functional, the title of “very first computer” often goes to ENIAC. First commercial samplesWith their enormous dimensions and design complexity, computers were available only to military departments and large universities, which assembled them themselves. But already in 1942, K. Zuse began work on the fourth version of his brainchild - Z4, and in July 1950 he sold it to the Swedish mathematician Eduard Stiefel. And the first computers that began to be mass produced were models with the laconic name 701, produced by IBM on April 7, 1953. A total of 19,701 of them were sold. Of course, these were still machines intended only for large institutions. In order to become truly widespread, they needed a few more important improvements. So, in 1955, on March 8, the “Whirlwind” went into operation - a computer that was originally conceived during the Second World War as a simulator for pilots, but by the time of its creation it arrived in time for the beginning of the Cold War. It then became the basis for the development of SAGE, an air defense subsystem designed to automatically target interceptor aircraft. Key Features"Vortex" became available random access memory 512 bytes and output graphic information on the screen in real time.
Technology to the massesThe TX-O computer, introduced in 1956 at MIT, was the first to use transistors. This made it possible to greatly reduce the cost and dimensions of the equipment. The team of scientists who developed the TX-O then left the institute, founded Digital Equipment Corporation, and introduced the PDP-1 computer in 1960, ushering in the era of minicomputers. They were no larger than one room or even a closet, and were intended for a wider range of clients. Well, the company began to produce the first desktop computers Hewlett Packard in 1968. Computers, without which our life is not possible, actually appeared not so long ago. Representatives of the older generation not only did not use computers during their studies at schools and institutes, but, as a rule, they had no idea what they were. The era of computers and even electronic computers - computers - as the first computers were called in our country, came into our lives relatively recently. Although their most distant predecessor, the abacus (abacus), appeared in ancient Babylon 3000 BC. Reconstruction of a Roman abacus The first person who invented the first digital computing machine was Blaise Pascal. In 1642, he introduced the Pascalina, the first mechanical digital computing device to actually be realized and become famous. The prototype device added and subtracted five-digit decimal numbers. Pascal produced more than ten such calculators, and the latest models operated on numbers with eight decimal places. It all started with this discovery...
Since then, many mechanical devices have been invented that make it possible to perform not very complex calculations. The main progress was observed from the end of the 19th century, and the peak occurred in the first half of the 20th century. And so, in 1938, the German engineer Konrad Zuse created the more complex first mechanical programmable machine Z1. On its basis, in 1941, he created the first Z3 computer, which has all the properties of a modern computer.
Who and when invented the first electronic computer? After all, he is the real prototype modern computers. And this happened quite soon after the invention of Konrad Zuse. In 1942, American physicist John Atanasov and his graduate student Clifford Berry developed and began installing the first electronic computer. The work was not completed, but had a great influence on the creator of the first electronic computer, ENIAC. The person who invented the ENIAC computer, the first electronic digital computer, was John Mauchly, an American physicist and engineer. John Mauchly generalized the basic principles of computer construction based on the experience of developing machines, and in 1946 the real electronic computer ENIAC appeared to the world. The development leader was John von Neumann, and the principles and structure of the computer he outlined later became known as von Neumann.
So the questions about what year the computer was created, where the first computer was created and who created the first computer can be answered in different ways. If we are talking about the first computer in general (in this case, a mechanical one), then Konrad Zuse can be considered its creator, and the country in which the first computer was invented can be considered Germany. If we consider the first computer to be an electronic computer, then it will be ENIAC, the inventor, respectively, is John Mauchly, and the country is the USA. The first computers were still far from the ones we use now - personal computers. They were huge, occupied significant areas, comparable to the area of a multi-room apartment, and weighed several tens of tons! Personal computers (PCs) appeared much later. Who then created the first personal computer? The creation of the first personal computers became possible only in the 1970s. Some people began to assemble computers at home for the sake of research interest, since there were practically no useful uses for computers at home. And in 1975, the first personal computer Altair 8800 appeared, which became the first commercially successful PC. The creator of the first personal computer was the American engineer Henry Edward Roberts, who was also the founder and president of Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems, which began producing the first PC. Altair 8800 was the “chief” of the boom in computerization of the population.
The first personal computers, and even the computers of the early 90s, were many orders of magnitude weaker than modern ones. Suffice it to say that the memory capacity of a modern, not-so-cool “flash drive” is comparable to the entire disk memory of several thousand (!!!) personal computers of the early 90s. And so it is the same for all other indicators. The fantastic leap in the performance of modern personal computers in the 2000s is associated primarily with the development of new technologies in the field of electronics and nanotechnology. Today, the computer has become an integral part of every person's life. This device is available in every home, and often not even one. Any workplace equipped with a computer in one format or another. The PC has long become commonplace and an obvious item of work and home use. And, of course, no one remembers for a long time what the very first computer in the world was like, and yet the process of evolution to miniature, but powerful devices didn't take that long. However, the device has undergone enormous changes. So, let's take a short excursion into history and remember how and when the first computer appeared. Before moving on to the question of when the first computers appeared, it is worth talking about those inventions of mankind that were made earlier and made a significant contribution to the main achievement.
Unfortunately, Z3 was destroyed in May 1945 when Russian troops entered Germany. But today in one of the museums in Munich you can see a recreated copy of it. The mechanism is striking in its size and it is already very difficult to compare this colossus with modern miniature gadgets. ENIAC - the very first computer in the worldWhat is ENIAC? Literally, it is an electronic numerical integrator and calculator. This machine was the first proof that it was actually possible to create a computer. What electronic machine capable of performing complex calculations. And that this is only the beginning of the greatest discoveries and developments. History of the ENIAC projectThe development of the very first computer in the world began in 1943. At the height of the Second World War, the United States required large volumes of calculations of firing tables, without which artillery could not hit the target accurately. At that time, this responsibility was assigned to women; calculations were performed manually using adding machines. In terms of time, such calculations took up to 16 days per calculation. To fully calculate one table, a large number of computers were involved and a lot of time was required.
In 1942, the University of Pennsylvania in the USA was offered a design for the first electronic computer based on vacuum tubes and a proposal to build it. The institute's management did not appreciate the project and sent it to the archives. Subsequently, the Ballistic Laboratory became interested in the computer. Such a solution would significantly speed up the calculation of shooting tables from several days or even months to several hours. In 1943, the project, again recreated from memory by the developer, was presented to the scientific department of the Ballistic Laboratory. To prevent the innovation from being rejected by the military, the machine was called an electronic differentiated analyzer. The representatives of the commission were very familiar with the mechanical analyzer and got the impression that the engineers simply wanted to make it electronic. According to the developers, the future machine will be able to calculate the firing trajectory in 5 minutes. The idea was approved and funds in the amount of almost 62 thousand US dollars were allocated to create the world's first computer. In the first development document, the machine was called “Electronic Numerical Integrator”; the additional word “Computer” was added to it a little later, after which the well-known and most famous abbreviation in the history of PC creation was formed. In February 1944, all the drawings and diagrams of the future vehicle were drawn up. And a group of engineers under the leadership of the main developers was ready for the final assembly and implementation of the project. In the summer of the same year, two test modules were assembled into one device, which were used to add numbers. They multiplied two numbers and gave the correct answer; the results of the experiment were provided to the management of the institute and laboratory and confirmed that the engineers’ project was completely feasible.
ENIAC was finally assembled in 1945 at the end of the war and was no longer useful for military purposes. In this regard, the American military department decided to use the machine’s capabilities in calculations for the development of thermonuclear weapons. ENIAC was presented to the public only a year later. It successfully carried out its work for 10 years and was permanently disconnected from power in October 1955. How the computer was usedTen years of continuous service is a very impressive period for the first computer. What did ENIAC manage to accomplish during this period?
Despite the length of time, the very first computer in the world produced very impressive results. Design characteristicsIn total, the creation of ENIAC cost almost 500 thousand US dollars and 200 thousand man-hours. The design consisted of 17.5 thousand lamps of 16 types, 7.2 thousand silicon diodes, 1.5 thousand relays, 70 thousand resistors and 10 thousand capacitors. The machine absorbed so much electricity that during the calculations, the nearest city was left without electricity for many hours. ENIAC had the following parameters and characteristics:
To calculate multiplication, the machine used repeated addition, so the power in this direction of calculations is reduced. All calculations were performed in the decimal system, and the binary system was familiar to the developers, but they preferred the first (he’s not in the photo below - just a picture for atmosphere)
To solve each specific problem, ENIAC was recommuted until 1947, that is, programmers re-formed a program to calculate a new problem by rearranging blocks and commutators. Then each calculation task was used as a subroutine, which greatly simplified programming the machine. Development teamSo, who is the developer of the first computer? The authorship of the main project belongs to John Presper Eckert and John William Mauchly. A whole group of highly qualified specialists worked directly on the creation of the machine.
In addition to these specialists, a team of programmers consisting of six girls worked on the computer:
Thus, it is difficult to determine who the creator of the ENIAC computer is in the singular. Many specialists worked on both the design and creation of computers. Further developments and creation of the first personal computersIn 1945, the first report was provided from EDVAC, Von Neumann's improved version of the first computer. He performed calculations not only using punched cards, but also using his own memory, this reduced the number of lamps and speeded up the calculation process.
The first PCs for sale appeared after the creation of microprocessors. IBM tried to organize the first sales already in 1974. But the devices were not in demand at all. These devices used cassettes as memory, and the cost of the machines was no more and no less - 10 thousand US dollars. Hence the lack of demand. The answer to the question who created the first computer accessible to home use, is obvious from the name of the machine - IBM 5100. This machine had a memory of 64 KB and could run some programs. Despite the cost and unclear purposes of use, the first sales still took place. Domestic developmentsEngineers in the Soviet Union also did not sit still and developed their own product. Who created the computer in the USSR? The project was led by S. A. Lebedev. Work began in 1948. The car was built only towards the end of 1950. And already in 1952, serious calculations of scientific and technical problems were carried out on Soviet MESMs. It is worth noting that when creating the very first computer in the USSR, Lebedev, independently of Von Neumann, came to the decision of using a program stored in memory to perform calculations. Despite the fact that Small electronic calculating machine It had low performance and a small amount of memory; it had fairly developed algorithms. It also had a storage device for long-term storage commands and immutable constants. History of computer gamesI wonder what the very first game in the world was? It was created in 1962 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Of course, the development of this product was carried out by engineers during non-working hours. The first game was called Spacewar. The plot is based on a battle between two space liners that attack each other with special missiles. The game was launched on a separate processor with a speed of 100 thousand operations per second and a memory of 9 KB.
A star map with liners was displayed on the display. The gun was controlled and fired using joysticks and a keyboard. The number of missiles each enemy had was limited, which added excitement to a simple shooter. Each player had to not only hit the enemy, but also avoid his attacks. It was possible to maneuver between stars or make hyperjumps in space.
The game was released commercially, and it was planned to make a good profit from the product. But the toy never gained much popularity, although it made its creators famous in narrow circles. Nevertheless, subsequent developments in this direction were already in demand. The creation of ENIAC, the very first computer in the world, was the start of developments in the direction of electronics and computer technology. Today, humanity has achieved quite a lot of success, but progress does not stand still and sometimes it is difficult to even imagine what awaits us ahead. |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Problems when using two operating systems and uninstalling one of them
- Boot in UEFI mode or legacy BIOS mode
- RAM Volumes and channels
- How to restore Windows if there are no restore points
- Charging a mobile phone with one battery
- How to increase volume through apps
- How to disable the Protect protection system in the Yandex Browser
- PGP encryption: what is it and how to use it
- avi file won't play - how to fix it
- Recovering deleted programs on your computer